Title: Prediction of tactile perception from vision on deformable objects
Authors: Brayan S. Zapata-Impata and Pablo Gil
Workshop: Robotic Manipulation of Deformable Objects (ROMADO), 25 October – 25 December, 2020
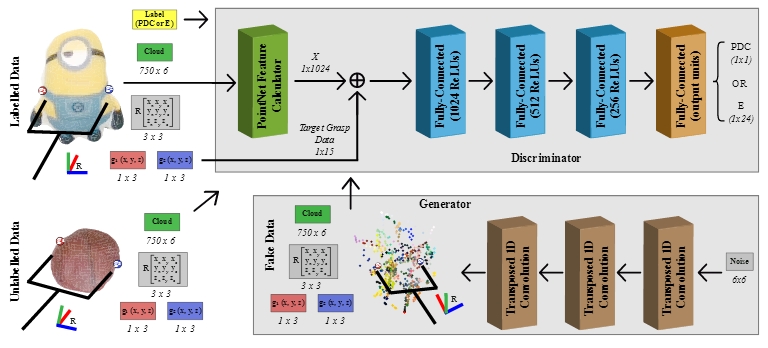
Abstract: Through the use of tactile perception, a manipulator can estimate the stability of its grip, among others. However, tactile sensors are only activated upon contact. In contrast, humans can estimate the feeling of touching an object from its visual appearance. Providing robots with this ability to generate tactile perception from vision is desirable to achieve autonomy. To accomplish this, we propose using a Generative Adversarial Network. Our system learns to generate tactile responses using as stimulus a visual representation of the object and target grasping data. Since collecting labeled samples of robotic tactile responses consumes hardware resources and time, we apply semi-supervised techniques. For this work, we collected 4000 samples with 4 deformable items and experiment with 4 tactile modalities.